Quantum Patents Analysis
Published:
Recently, quantum computing has drawn the attention of many companies around the world. This article aims to present an overview of quantum existing patents.
Methodology
The following analysis is based on the extraction of the WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organization). The analysis is focused on patent families which regroups patents covering the same technical content. The study is restricted to patents committed under classfication G06N 10/00 named “Quantum computing, i.e. information processing based on quantum-mechanical phenomena”. The full IPC (International Patent Classification) can be found here.
The WIPO offers a web interface to perform advanced patent search and extract the research output into a csv file (with a limitation of 10,000 lines). The reader can carry out his own research on WIPO’s patentscope tool. The source code and sample of data used for this study can be found on github.
The data extraction was done on 04/2022.
Global numbers
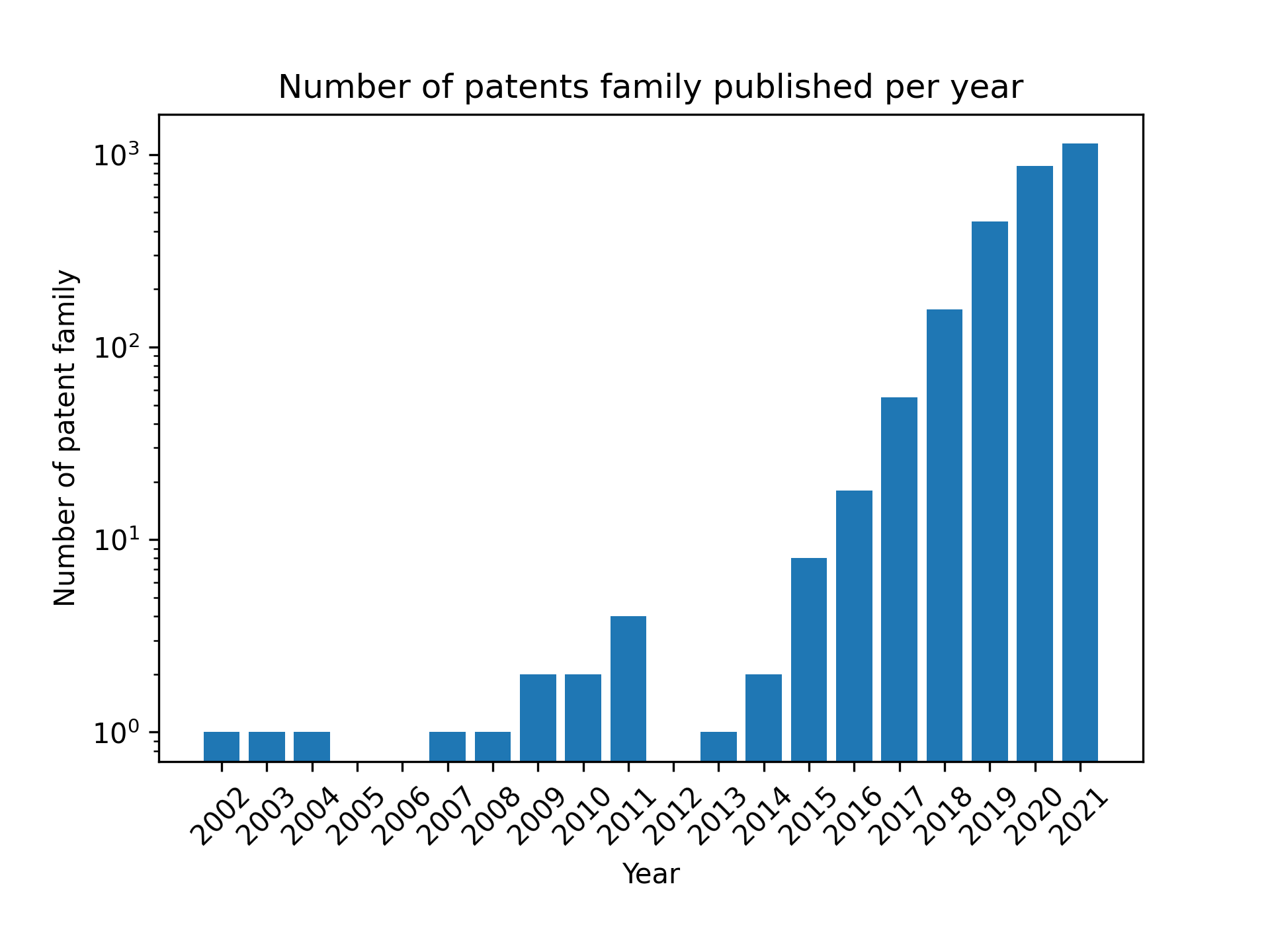
The extraction of patents classified under G06N 10/00 IPC has provided 2 700 different and unique family of patents. The figure below shows the number of quantum patent families published the last 20 years using a logarithmic scale. Since 2015, the number of families nearly follows an exponential law, passing from about 10 patents per year in quantum computing field to more than 1000.
With 10 companies in the top 15 first publishers in quantum field, the United States of America is currently way beyond all other countries for the deposit of patents on this technology.
Table 1. Number of families of patents per applicants (Top 15)
| Rank | Company name | Number of families of patent | Headquarter | First patent published on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IBM | 381 | Armonk (United States) | 28/01/2016 |
| 2 | 138 | Mountain View (United States) | 22/06/2017 | |
| 3 | Microsoft | 119 | Redmond (United States) | 03/02/2016 |
| 4 | HeFei Benyuan Quantum Computing Technology | 117 | Hefei, Anhui (China) | 01/05/2018 |
| 5 | Intel | 94 | Santa Clara (United States) | 03/01/2019 |
| 6 | D-Wave | 86 | Burnaby, British Columbia (Canada) | 10/07/2003 |
| 7 | BAIDU NETCOM Science and Technology | 76 | Beijing (China) | 07/06/2019 |
| 8 | IONQ | 54 | College Park, Maryland (United States) | 25/04/2019 |
| 9 | Rigetti | 47 | Berkeley, California (United States) | 06/10/2016 |
| 10 | Northrop Grumman systems | 45 | Los Angeles (United States) | 06/04/2011 |
| 11 | University of science and technology of China | 35 | Hefei, Anhui (China) | 21/05/2019 |
| 12 | Equal1 | 32 | San Carlos, California (United States) | 26/12/2019 |
| 13 | MIT | 31 | Cambridge, Massachusetts (United States) | 18/05/2017 |
| 14 | Zapata Computing | 31 | Boston, Massachusetts (United States) | 09/01/2020 |
| 15 | Tsinghua University | 31 | Beijing (China) | 13/11/2018 |
The United states and China are both the most targetted countries by applicants. About 25% of the patent families covers the whole world. European region and other countries remain way behind these 3 main targets of applicantion.
Table 2. Number of patent families according to their region of application
| Region of application | Number of patent families |
|---|---|
| UNITED STATES OF AMERICA | 1319 |
| CHINA | 712 |
| WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION | 669 |
| EUROPEAN PATENT ORGANIZATION | 72 |
| REP KOREA | 52 |
| JAPAN | 39 |
| GERMANY | 24 |
| UNITED KINGDOM | 16 |
| CANADA | 16 |
| AUSTRALIA | 14 |
| FRANCE | 6 |
| RUSSIAN FEDERATION | 4 |
| ISRAEL | 4 |
| NETHERLANDS | 3 |
| FINLAND | 3 |
| INDIA | 3 |
Table 3. Earlier publishers of quantum patents
| Company name | Publication date of the first patent | Title of the patent |
|---|---|---|
| D-Wave | 10/07/2003 | Quantum computing integrated development environment |
| Cooperman Gary | 30/10/2004 | Audioptical vortex replication transdigitator |
| QUCOR | 10/11/2010 | Control and readout of electron or hole spin |
| Northrop Grumman systems | 06/04/2011 | Method and apparatus for controlling qubits with single flux quantum logic |
| Element Six Tech | 06/04/2011 | Solid state material |
| National Research Council CANADA | 13/04/2011 | Atomistic quantum dots |
| Lockheed Martin Corporation | 01/05/2015 | Quantum-assisted training of neural networks |
| NewSouth Innovations | 23/07/2015 | Optical Quantum logic |
| Toshiba | 19/11/2015 | Photon source |
References
The reader may access following links and publications to get other point of views on quantum computing patents:
Alex, Mathew. “Quantum technologies: A review of the patent landscape.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04552 (2021)
